Aegna Island Infrastructure

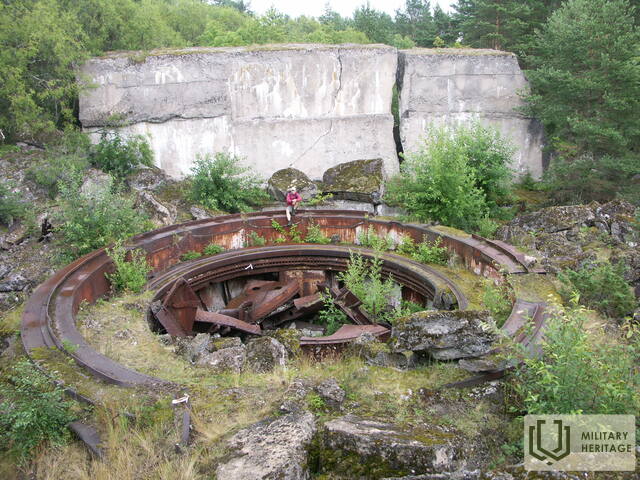
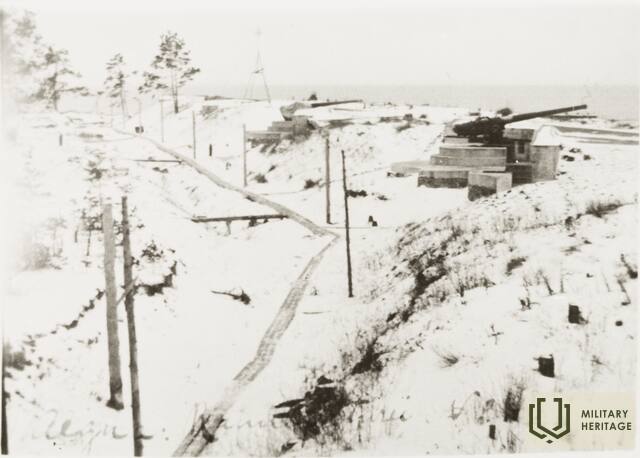
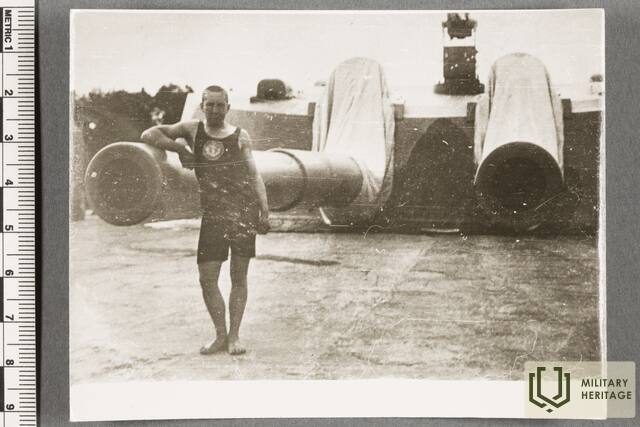
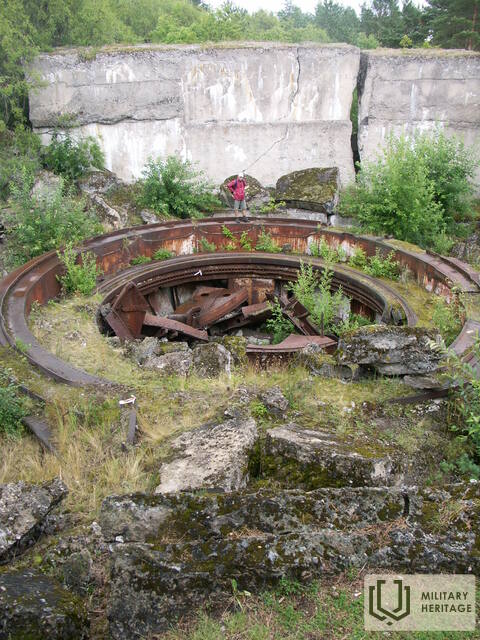
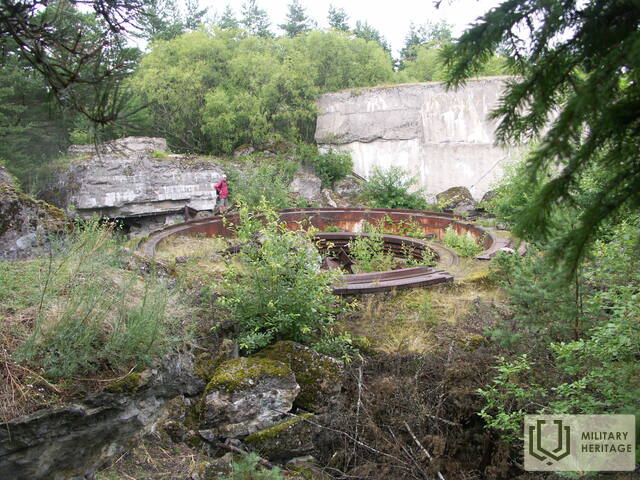
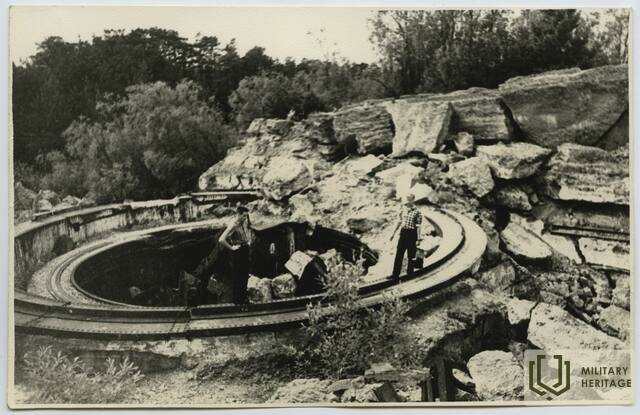
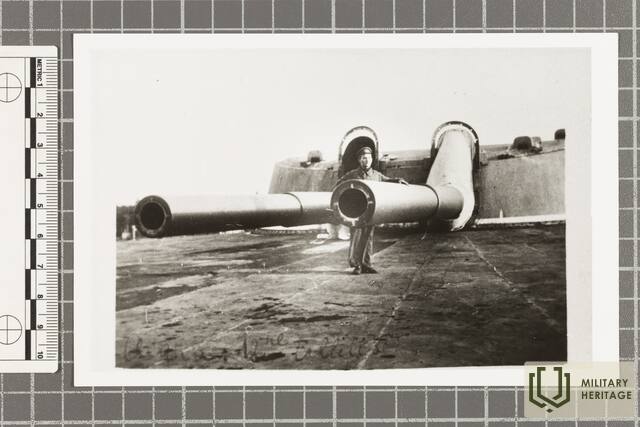
The three square kilometres of this island in the north-eastern corner of Tallinn Bay are the site of an extensive network of coastal defence batteries and a three-kilometre narrow-gauge railway built before World War I as a continuation of the fortification work begun by Peter the Great in the 18th century. Construction of the Alexander Nevsky Battery began in 1915. The 180-metre concrete structure was coupled at both ends with barbettes supporting two 12-inch guns each. The guns at the eastern end were higher than at the western end, allowing them to be fired westward over the other guns. Battery No. 3 was built on the western shore of Aegna and was ready for combat by autumn 1916. The battery was first planned to have six 130-mm guns, but in the end it was only equipped with four.
In 1918, following the declaration of the independence of Estonia, the coastal defences were taken over by the Estonian Navy. The island had residential housing, barracks, an officer’s mess, staff headquarters, a bread factory, a library, a clinic, a bathhouse and more. The command centre on the island was completed in 1927 in Eerikneeme. Battery No. 10 was also completed that year, equipped with three 75-mm anti-aircraft guns (with a barrel length of 3.75 m) capable of firing up to 6 km in altitude. The importance of Aegna in the coastal defence of Estonia is reflected in the fact that, at its peak, half the men serving in the Naval Fortress Division were stationed on the island. The existing infrastructure enabled the locals to manage on their own in winter, since disruptions to sea traffic were common.
After World War II, the Soviet Navy Baltic Fleet Air Defence branch, consisting of around 100 marines, was stationed on Aegna until 1957. A new anti-aircraft battery made up of four concrete gun pits 45 metres apart were constructed near the Alexander Nevsky Battery searchlight bunker in the north-western part of the island. Bofors 40-mm guns formerly used by the Estonian military were installed. Due to the Estonian coastline being a restricted area during the Soviet era, travelling to Aegna only became possible again in the 1960s. Traces of different military periods are still clearly visible on the island.